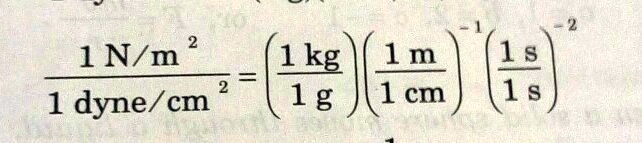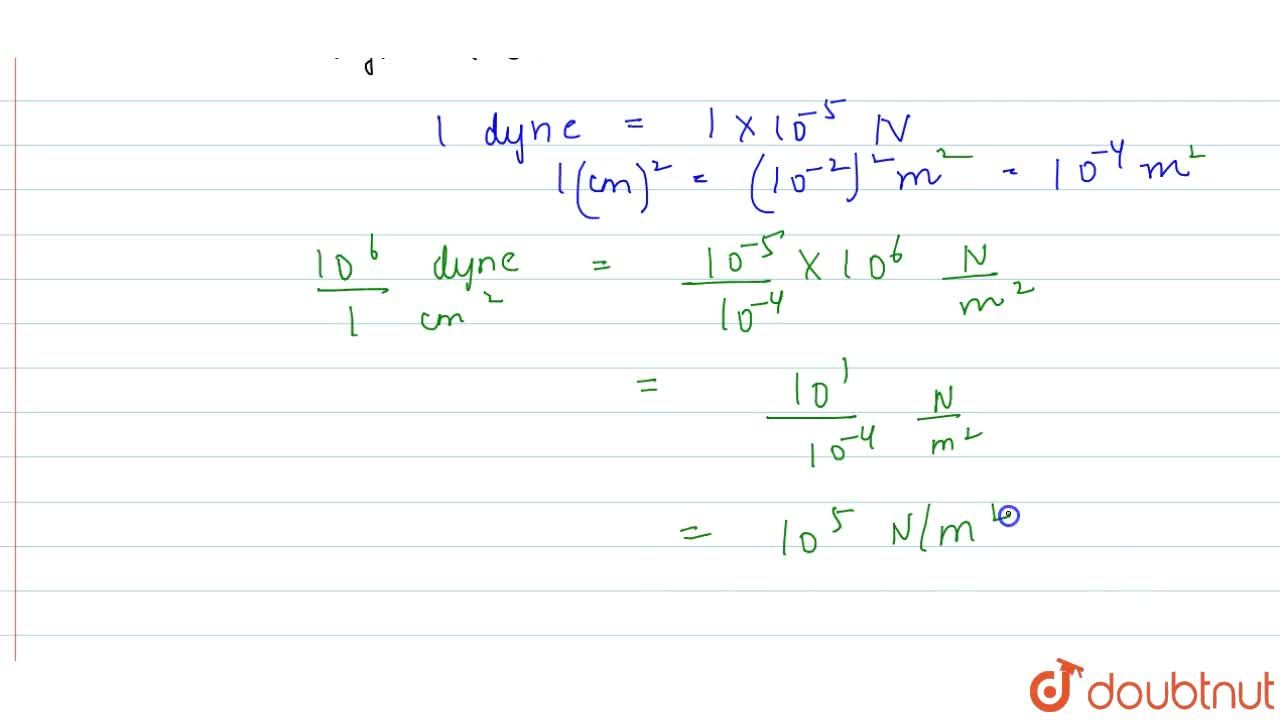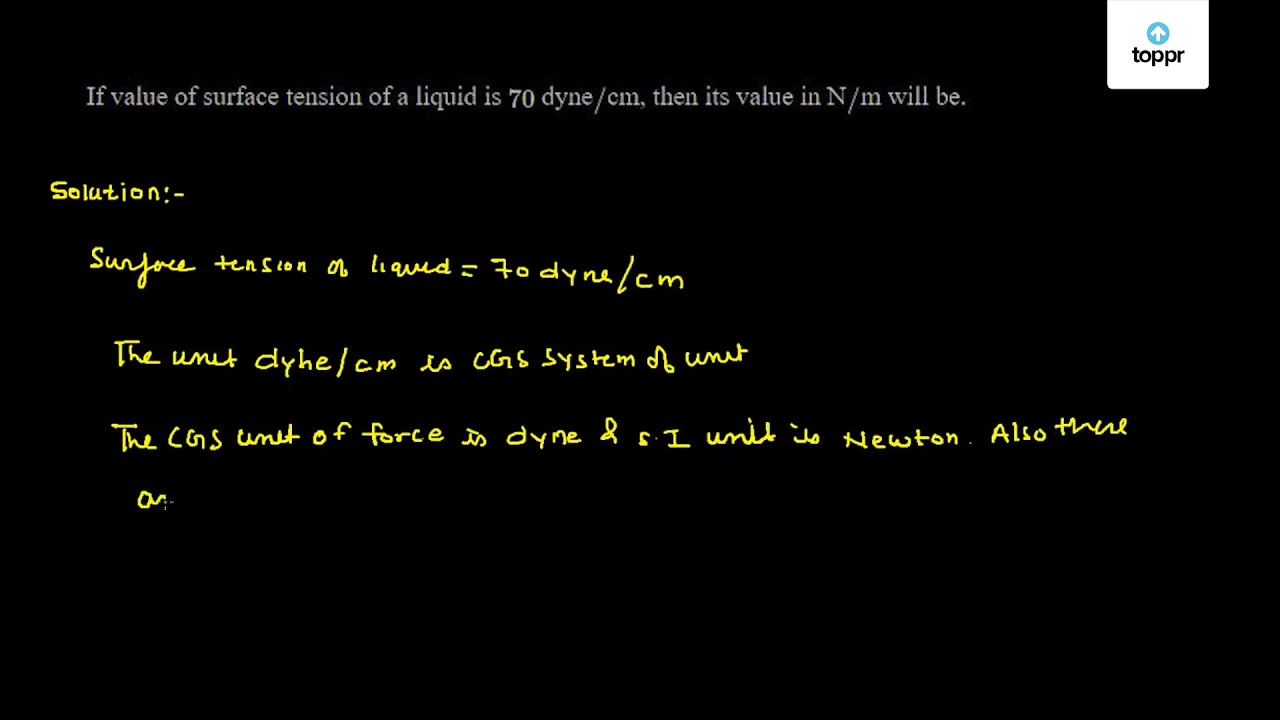The Young's modulus of steel is `1.9 xx 10^(11) Nm^(-2)` . Calculate its value in dyne `cm^(-2)`. - YouTube

If the value of atmospheric pressure is `10^(6)` dyne `cm^(-2)`, find its value in SI units. - YouTube

Young\'s modulus of steel is `19xx10^10 N/m^2`. Expres it indyne/cm^2. Here dyne is the CGS unit... - YouTube
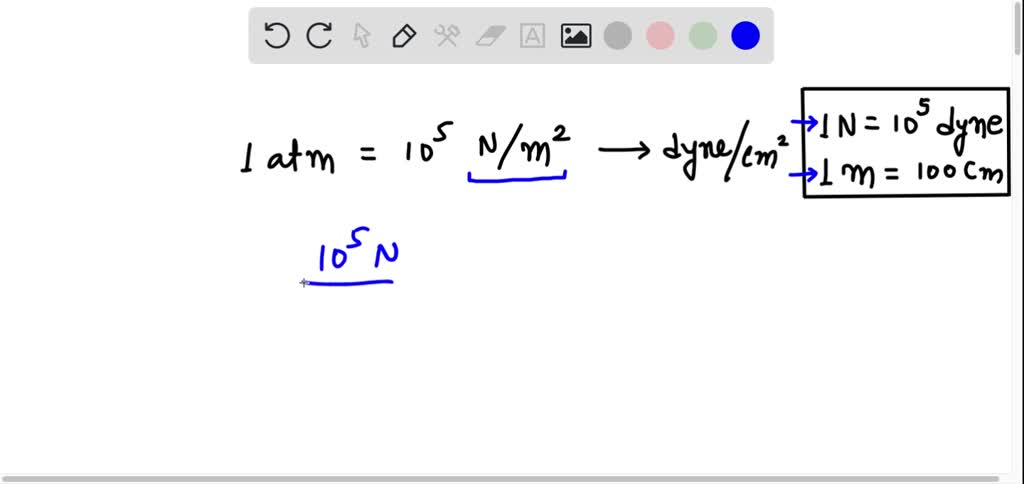
SOLVED: Convert one atmospheric pressure 10 to the power 5 Newton per metre square into dyne per cm square